Campus networks consist of multiple local area networks (LANs) within a limited geographical area. A campus network is wider than an individual LAN but smaller than a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN).
Ideal for large campuses with thousands of students and staff, this system allows administrators to centrally manage access points and device policies from a central location – further simplifying and improving security.
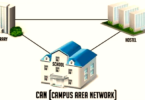
Topology of Campus Area Network
Campus Area Networks (CANs) are networks that interconnect networks within a specific geographical locality, such as university campuses, organizational campuses, or military bases. A CAN consists of various local area networks (LANs) connected via special networking hardware like routers and switches and is capable of fast data transfers without disrupting system performance; additionally, it can also provide internet connection services.
CAN is often found in educational institutions like schools and universities, enabling both students and staff to share files and resources efficiently. Furthermore, its reliability makes it suitable for use at remote work sites like oil rigs or research stations that rely on reliable connections; additionally, CAN technology may even support augmented reality training or autonomous vehicles.
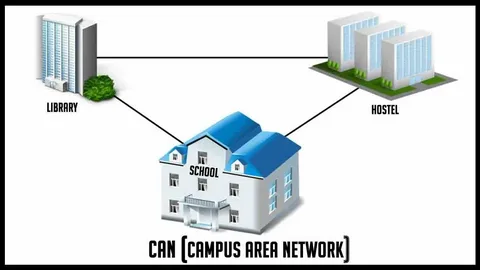
CANs can be connected via various means, including twisted pair cables, optical fiber, and wireless networks. The network topology used will depend on the layout and needs of each site; while physical structures of CANs may change with each location’s needs, its logical network remains independent from physical ones and must comply with certain standards to protect sensitive information.
A CAN can take many different forms, but all must adhere to the OSI model for effective communication between devices. Furthermore, its design must allow for future expansion while remaining secure against attacks from hackers.
CAN is also popular among businesses that need to send large volumes of data quickly, such as businesses that upload videos online; uploading one can take hours with traditional means but CAN does it in minutes, meaning companies can use it to connect offices and employees even if they reside in different buildings.
CAN is the ideal network solution for colleges, hospitals, and large corporations with multiple buildings that require interconnection. It is the fastest network for sharing large files at lightning speed while offering a superior experience compared to WAN or MAN networks; additionally, it provides secure storage of confidential information. CAN can easily be set up and maintained while being accessible to anyone who can connect to the Internet.
Security of CAN
CAN networks are often found connecting college campuses but can also be found in large office buildings and military bases. These networks are designed to be as secure as possible and offer many advantages over other types of networks – for instance, they’re easy to maintain without the same limitations that WANs or MANs might. They also offer more privacy when transmitting data.
Since CAN networks are usually managed by one IT team, security policies, and access points can be managed centrally from a central location, helping reduce patch and change requests from individual devices while assuring all devices remain up-to-date with best practices for online security.
CAN also offers another advantage: its wireless communication across large areas. This capability is particularly relevant to campus universities with thousands of students and staff, where wireless communications are essential to supporting campus life. CAN can ensure this capacity by offering secure segmented access for both students and faculty members alike.
Additionally, CAN can boost network speed and reliability by using less bandwidth. This is achieved by breaking data up into packets, with each one holding only limited amounts of information, or by creating a firewall to block out unwanted traffic from entering.
While CAN is an excellent choice for large schools and corporate campuses, it does have some limitations. For example, it can be challenging to detect and protect against security threats, and its networks rely on physical infrastructure like cables and Wi-Fi access points – any disruption in these systems could compromise network performance and connectivity.
CAN networks can be an ideal solution for organizations needing to manage multiple LANs in a limited geographic area. However, they are less flexible than their WAN or MAN counterparts and may be costly to set up and maintain – this often makes CAN networks preferable among larger organizations.
Transfer of data in CAN
A Campus Area Network, or CAN, is an IT network connecting buildings within a campus to facilitate data transfer with high speeds and security. Copper wires or optical fibre connect it securely and allow centralized management. Furthermore, its use extends outside its confines for communication with external networks or devices while its central management provides improved performance and security.
CANs can be created using various hardware devices, including hubs and switches, with limited nodes that use less bandwidth than their LAN/WAN counterparts. Furthermore, this network is easy to maintain. It provides high-speed connectivity, typically used in schools and universities as well as large organizations and industrial sites – also used by some automotive applications.
CAN networks are an attractive option for college campuses because they provide high-speed connectivity between buildings, supporting large numbers of users with centralized management and providing increased security as well as faster application access.
Contrasting other networks, CANs offer advantages over LANs in that they support wider geographical areas yet still remain smaller than Metropolitan Area Networks and Wide Area Networks. This makes managing them simpler for IT administrators while potentially helping reduce IT service costs.
Additionally, adding devices to a CAN network without increasing its size is possible; this network can be created by connecting multiple LAN networks using routers and switches. It is often used between departments within an organization as well as providing wireless connections between different buildings. In fact, its usage even extends into vehicles, often being known as an “automotive network”.
The CAN is an integral component of IT infrastructure and facilitates data transfer between devices. Its use enables better coordination of resources and increases overall efficiency within organizations; furthermore, quality IT service delivery remains vitally important in today’s digital economy.
Read More:
The Future of Campus Area Networks
Maintenance of Campus area network
Campus area networks (CANs) are computer networks that connect several local area networks (LANs) across a large area, generally found in universities, business parks, hospitals, and military bases. They typically utilize high-bandwidth backbone links for data transfer between nodes; additionally, they’re managed centrally.
It can enable network administrators to remotely control all devices and access points from one central point, offering greater security and control for greater organization efficiency. By consolidating maintenance tasks across systems, organizations save both time and resources by reducing maintenance requirements, while firewalls help protect private information against hackers gaining entry.
To keep a CAN running smoothly, it is essential to understand how they operate and what to look out for. CANs are connected using routers, switches, hubs, copper wires, or optical fibers and are used to transfer data between local area networks (LANs). They may be used for various purposes, including providing internet service on college campuses as well as connecting classrooms or other facilities within them.
Can offer another great benefit: their flexibility. Scalability makes CANs ideal for colleges, medical centers, and other institutions that want to expand their services quickly.
CAN architecture is also ideal for large enterprises that need wireless coverage in both indoor and outdoor areas, such as insurance or technology companies that need access for thousands of staff across multiple buildings. Can help these enterprises accomplish this goal by offering secure yet segmented access for employees.
CANs can be simple to maintain if handled by an experienced IT team. Network administrators can implement security policies across the whole CAN by setting login requirements, blocking unsafe devices, and creating other safeguards. Furthermore, CANs help IT teams more efficiently manage their networks than using multiple isolated networks.