Computer Network
A Computer Network is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networked computing devices exchange data with one another by the usage of a data link. The connections between nodes are set up with the use of either cable media or wireless media. The well-known computer network is the Internet.
Network computer devices that originate, route, and terminate the records are called network nodes. Nodes can encompass hosts consisting of personal computer systems, telephones, and servers, in addition to networking hardware. Two such devices can be said to be networked together when one tool is capable of exchanging information with the other tool, whether or no longer they have an immediate connection to one another.
Computer networks vary inside the transmission medium used to carry their indicators, the communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network’s size, topology, and organizational reason.
Computer networks support a large number of programs and services along with admission to the World Wide Web, digital video, virtual audio, shared use of software and storage servers, printers, and fax machines, and use of email and immediate messaging programs, as well as many others. In maximum cases, application-unique communications protocols are layered over other extra well-known communications protocols.
Properties
Computer networking can be taken into consideration as a branch of electrical engineering, telecommunications, computer science, information era, or laptop engineering because it is predicated upon the theoretical and realistic utility of the associated disciplines.
A computer community enables interpersonal communications, permitting customers to talk efficiently and effortlessly via various means: email, immediate messaging, chat rooms, telephone, video telephone calls, and video conferencing. Providing get right of entry to facts on shared storage devices is an essential feature of many networks. A network allows the sharing of files, facts, and other styles of records, giving legal users the potential to get the right of entry to information stored on other computer systems on the network.
A community allows the sharing of network and computing resources. Users may also get entry to and use assets furnished via gadgets in the community, such as printing a file on a shared community printer. Distributed computing uses computing resources throughout a network to perform obligations. Computer crackers can use a computer network to install computer viruses or laptop worms on devices connected to the network or to save these devices from accessing the community through a denial of service assault.
Network packet
Computer communication links that do not support packets, such as traditional point-to-point telecommunication links, truly transmit data as a chunk circulation. However, most statistics in computer networks are carried in packets. A network packet is a formatted unit of information (a listing of bits or bytes, usually a few tens of bytes to 3 kilobytes long) carried by means of a packet-switched network.
In packet networks, the information is formatted into packets which might be sent through the community to their destination. Once the packets arrive, they may be reassembled into their unique message. With packets, the bandwidth of the transmission medium can be higher shared amongst customers than if the network had been circuit switched. When one consumer is only sometimes sending packets, the link may be full of packets from other users. So, the price may be shared, with particularly little interference, provided the link isn’t overused.
Packets consist of two kinds of data: control information and user data. The control information provides the network desires to supply the person statistics, for instance, supply and destination community addresses, mistakes detection codes, and sequencing information. Typically, control information is determined in packet headers and trailers, with payload facts in between.
Often, the course a packet needs to take through a network is not immediately to be had. In that case, the packet is queued and waits until a link is free.
Network nodes
Apart from any physical transmission medium there can be, networks contain additional primary system building blocks, which includes community interface controller (NICs), repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, modems, and firewalls.
Types of Networks
Many kinds of computer networks are categorized via the cause they serve; for instance, if it is for personal or instructional use, the dimensions/span of the community, or even the devices it connects. In this report, we are able to discuss the subsequent:
Personal Area Network (PAN).
A Personal Area Network is a computer network used to connect devices that are near a person’s individual. Examples of devices on a PAN network consist of: personal computer systems, wireless printers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), video game controllers, cell phones, and so on. PANs can connect devices inside a very small radius, about 20- 30 feet, and maybe both a wired or wireless connection.
Local Area Connection (LAN).
A LAN may be both wired or wireless and is a computer network that covers a reasonably small area, including a home, office, or small organization of buildings, which includes a library or airport. A higher data transfer rate and smaller area of coverage sets a LAN apart from all other computer networks.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
MANs connect more than two nearby location networks or campus location networks with the aid of connecting routers, switches, and hubs in the area of a single city.
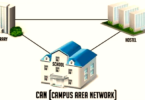
Campus Area Network (CAN).
A CAN is a connection of LANs within a restrained area along with a public institute campus. This kind of network often links educational buildings, the college/college library, or student dorms. It is similar to a MAN as it connects multiple LANs. Still, the distinction is that a CAN is commonly smaller than a MAN and is specific to an educational setting.
Wide Area Network (WAN).
A WAN is a network that covers a broad area; any network that crosses metropolitan, regional, or national barriers is considered a WAN. A WAN operates by connecting a couple of routers and public communications links, along with smartphone lines. The most commonly recognized WAN is the Internet, which most of the alternative computer networks additionally connect with.
Intranet
An intranet is a set of networks that is underneath the manage of a single administrative entity. The intranet uses the IP protocol and IP-based tools inclusive of net browsers and document transfer programs. The administrative entity limits the use of the intranet to its authorized customers. Most generally, an intranet is the internal LAN of an enterprise. A large intranet commonly has, as a minimum, one web server to offer users organizational information. An intranet is also anything behind the router on a local area network.
Extranet
An extranet is a network that is also below the administrative control of a single corporation; however, it helps a restrained connection to a selected external community. For example, a company can also provide access to a few elements of its intranet to share records with its business partners or clients. These different entities are only sometimes depended on from a security standpoint. Network connection to an extranet is often, however, only sometimes, applied via the WAN era.
Darknet
A darknet is an overlay network, generally running on the net, that is simplest accessible through specialized software. A darknet is an anonymizing network in which connections are made simplest among trusted peers — sometimes called “friends”— the usage of non-standard protocols and ports.
Darknets are distinct from other dispensed peer-to-peer networks as sharing is anonymous (that is, IP addresses aren’t publicly shared), and consequently, users can talk with little fear of governmental or corporate interference.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are many distinct styles of PC networks within the international nowadays. The alternatives range from stressed out to Wi-Fi to a network that only extends to a 20-30 foot radius to a network that could span throughout a whole nation. Networks enable you to print an essay while you’re in a unique room out of your printer or to email a pal or family member in every other kingdom. The technology we’ve got today is certainly excellent and will only continue to grow and connect human beings from all over the international. So next time you email an extended-misplaced pal who’s miles away, you could thank laptop networking for making it viable.
FAQs
- What is the number one purpose of a Local Area Network (LAN)?
LANs are designed to attach devices within a constrained geographical region, facilitating efficient verbal exchange and useful resource sharing amongst users.
- How can corporations mitigate protection worries in computer networks?
Implementing measures inclusive of robust passwords, normal updates, firewalls, antivirus packages, and employee education can beautify community protection.
- What role does 5G technology play in the destiny of computer networks?
The 5G era guarantees faster and greater dependable connectivity, enabling new opportunities in areas like augmented fact, self-sufficient motors, and smart cities.
- Are there any super examples of successful laptop community implementations?
Yes, several case research highlight successful implementations, demonstrating the superb impact of properly designed and maintained pc networks.
- How can individuals optimize their Personal Area Networks (PANs)?
Optimizing PANs involves efficaciously connecting and coping with personal devices, making sure seamless communique and aid sharing inside a man or woman’s workspace.