What is a Personal Area Network and How Does it Work?
Personal area networks connect all technology devices within an individual’s immediate environment, including smartphones, headphones and laptops.
These networks can be wired or wireless. Wired PANs use technologies like USB and FireWire; wireless ones connect through signals like Bluetooth, Zigbee and Ultra-Wideband.
There are even portable PANs that move with us, like the connection between a smartphone and Bluetooth headphones.
What is a personal area network?
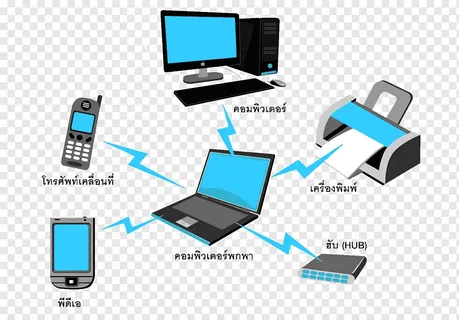
Personal Area Networks, or PANs, are small computer networks designed to link technology devices in an individual’s immediate environment together. This may include electronic equipment like computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones as well as entertainment gadgets like speakers and gaming consoles – as well as wearable technology devices like speakers. Wired PANs typically utilize cables like USB or Firewire, while wireless ones rely on close-range wireless technology protocols like Bluetooth and infrared for connection.
What is a Personal Area Network and How Does it Work?
PANs enable users to share data between technology devices within a small, closed network without connecting to the internet directly. They’re designed to seamlessly integrate into homes, offices, and work-from-home environments using various wireless networking technologies.
PANs offer several distinct advantages compared to more extensive computer networks such as LANs. Their low complexity and security is enhanced, plus their portability surpasses that of router- and switch-based networks; plus, they consume minimal energy consumption and can operate for extended periods using rechargeable or non-rechargeable batteries.
A key difference between a LAN and a PAN lies in their respective capabilities, while a LAN supports multiple computers and other electronic devices in a shared environment. In contrast, PANs typically only support one person and their devices due to limited range and network capabilities – typically having a radius of around 10 meters/33 feet and being restricted solely within their immediate surroundings.
Contrarily, LANs connect various electronic devices across the globe for data exchange with people at various locations. Furthermore, LANs support many technologies like gigabit Ethernet and wireless network protocols for greater reliability.
PANs do not typically include routers and cannot directly access the Internet; however, they can link up with a local area network (LAN), which then connects directly to it. For instance, desktop computers, wireless mouse, and headphones could all connect via PAN while only the computer could gain access to it directly.
How does a personal area network work?
Personal area networks (PANs) connect individual electronic devices, like computers and printers, directly without using traditional routers and switches as seen in larger networks; instead data transmission takes place using short-link radio technology such as Bluetooth. PANs make an ideal solution for homes as well as workspaces where many electronic devices are utilized together in close proximity.
PANs (Personal Area Networks) can be wired using computer bus technologies like FireWire and USB, or wireless through network technologies like Bluetooth, IrDA, INSTEON Z-Wave ZigBee etc. A PAN may even follow you around as you move throughout your home or office – for instance when connecting smartphones to bluetooth headphones wirelessly.
Personal area networks offer many advantages over other forms of computer networking, including centralizing data storage and printing operations, easy setup and maintenance procedures, and security that is limited to their immediate vicinity. There are a few key differences between personal area networks (PANs) and other forms of computer networking like local area networks (LANs) or wide area networks (WANs), however.
LANs and WANs utilize wired or wireless technologies like Ethernet or Wi-Fi, with either covering a much broader area than PANs which are restricted to users’ immediate surroundings and smaller than that. PANs tend to use lower data rate technologies than LANs/WANs such as Bluetooth and infrared;
To create a PAN, the devices to be interconnected must be compatible with each other and with the network as a whole. For instance, connecting desktop computer and printer requires using compatible communication protocols that both support wireless communications technology; both must also have access to the same network access password for effective collaboration. Some wireless devices that can form personal area networks include PCs, laptops, smartphones, tablets, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), video game consoles speakers wearable gadgets.
What are the real-world applications of a personal area network?
Personal Area Networks (PANs) connect information technology devices in an individual’s immediate environment, such as laptop computers, PDAs or tablet computers, cellphones and printers. PANs typically utilize wireless technologies like Bluetooth, WiFi or infrared to link devices together; they may also utilize wired technologies like USB or FireWire as links between them.
PANs (Personal Area Networks) can be used for data transmission between connected devices, or as gateways into higher level networks and the Internet, acting as gateway devices for access. PANs may also be utilized for communication, collaboration and remote control of home automation systems.
Personal area networks have many practical uses in everyday life. Some of the more popular examples include connecting mobile phones and computers for data sharing and streaming audio/video, or using smartphones as personal hotspots when away from home or work for internet access. Other applications may include synchronizing calendar appointments between multiple devices or sharing files and music between computers; PANs can even connect smart light bulbs or household appliances directly with tablets or smartphones, enabling users to control them via their interface.
A key difference between a Personal Area Network (PAN) and local area networks (LAN) is their differing connection capacities and user capacities; while LANs primarily use wired technologies like Ethernet to link devices together, while PANs utilize wireless technologies like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth for device connection.
Personal area networks (PANs) offer numerous advantages, from reduced costs and easy setup, to making collaboration between students and professionals simpler due to devices being accessible from any internet connection anywhere on their network. A PAN may even help facilitate home automation or security systems control systems.
Personal area networks do have some drawbacks, however. This may include limited data transfer rates and potential interference with radio signals. Furthermore, only devices compatible with its technology (for instance, a wireless PAN requires all devices be Bluetooth- or infrared-capable) may use it.
What are the disadvantages of a personal area network?
Personal area networks (PANs) are networks composed of devices connected by wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi or infrared for communication purposes. PANs are commonly found in homes, offices and small network areas for their flexibility and efficiency – although they do pose certain drawbacks that should be kept in mind before adopting one.
Personal area networks present one main drawback – their limited network range. Devices within that zone of origin cannot connect, which could become problematic when constantly moving around your home or office space.
Personal area networks also suffer from limited data transmission rates; Bluetooth-based technologies cannot transmit large volumes of data at high rates, rendering them unsuitable for applications that demand large bandwidth capacities. Finally, personal area networks may be susceptible to interference from nearby wireless devices that may result in data loss or system failure.
Although personal area networks (PANs) have limitations, they can still be an invaluable asset in certain circumstances. If you work from home, PANs provide easy and quick access to shared files and documents from colleagues; additionally, they connect mobile devices or computers directly to televisions or speakers for multimedia playback, as well as sharing media between multiple devices within your home or office – provided a strong password is in place and all devices remain up-to-date with security updates – in order to protect against vulnerabilities which might compromise a PAN from becoming compromised!